Understanding the Poorest U.S. State
Determining the poorest U.S. state is crucial for understanding socioeconomic disparities and allocating resources effectively. Poverty levels are influenced by various factors such as unemployment rates, income levels, cost of living, and access to education and healthcare.
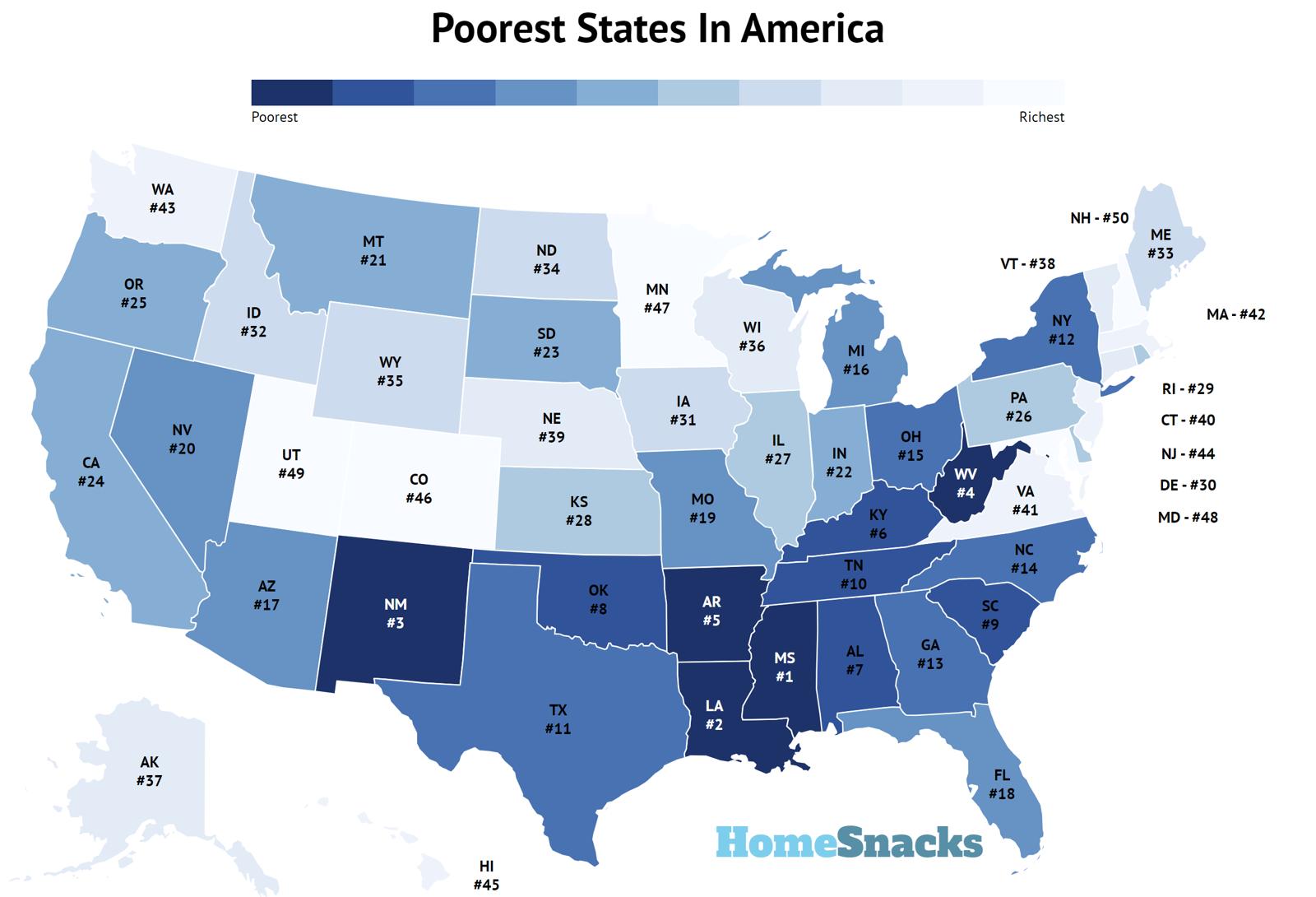
Analyzing poverty data from the U.S. Census Bureau and other reputable sources, Mississippi consistently ranks as the poorest state in the nation. It faces significant challenges, including a persistently high poverty rate, low per capita income, and limited economic opportunities.
Addressing poverty requires a multifaceted approach involving government policies, community initiatives, and individual empowerment. Understanding the poorest U.S. state is a critical step towards developing targeted interventions and fostering economic growth.
What is the Poorest US State?
Understanding the poorest US state requires examining various socio-economic factors. Here are 10 key aspects:
- Income: Low per capita income and household earnings
- Poverty rate: High percentage of population living below the poverty line
- Education: Limited access to quality education and low literacy rates
- Healthcare: Lack of affordable healthcare and limited access to medical facilities
- Employment: High unemployment rates and low job availability
- Housing: Inadequate housing conditions and lack of affordable housing
- Infrastructure: Poor infrastructure, including transportation, water, and sanitation
- Food security: Limited access to nutritious food and high rates of food insecurity
- Safety: High crime rates and lack of public safety
- Economic opportunity: Low levels of business investment and limited job growth
These aspects are interconnected and contribute to the overall poverty levels in a state. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive policies that promote economic development, improve education and healthcare access, and provide social safety nets for vulnerable populations.
Income
Income levels play a significant role in determining the poorest US state. Per capita income, which represents the average income earned per person in a state, and household earnings are key indicators of economic well-being. Low per capita income and household earnings are often associated with poverty, as they limit individuals' and families' ability to meet basic needs such as food, housing, and healthcare.
In the context of identifying the poorest US state, low income levels can be a major contributing factor. States with persistently low per capita income and household earnings may struggle to provide adequate public services, support education and healthcare systems, and attract businesses and investment. This can create a cycle of poverty, where low income levels perpetuate limited opportunities and hinder economic growth.
Addressing income inequality and promoting economic development are crucial steps towards reducing poverty. Policies that focus on job creation, skills training, and affordable housing can help boost incomes and improve the overall economic well-being of a state.
Poverty rate
The poverty rate, which measures the percentage of a population living below the poverty line, is a key indicator of the economic well-being of a state. A high poverty rate is a significant factor in determining the poorest US state, as it reflects the extent of economic hardship and social inequality within a state.
- Lack of economic opportunities: A high poverty rate can indicate a lack of economic opportunities and job growth within a state. When individuals and families have limited access to well-paying jobs, they may struggle to meet their basic needs, leading to poverty.
- Inadequate education and skills: Poverty can perpetuate itself through inadequate education and lack of job skills. Individuals living in poverty may have limited access to quality education, which can hinder their ability to acquire the skills necessary for higher-paying jobs.
- High cost of living: A high cost of living, relative to income levels, can contribute to poverty. When the cost of housing, food, and other necessities is high, individuals and families may struggle to make ends meet, even if they are employed.
- Lack of affordable housing: The lack of affordable housing can also contribute to poverty. When housing costs are high, individuals and families may be forced to live in substandard or overcrowded housing, which can have negative impacts on their health and well-being.
Addressing poverty requires a multifaceted approach that includes policies to promote economic growth, invest in education and job training, and provide affordable housing. By tackling the root causes of poverty, states can work towards reducing the poverty rate and improving the overall well-being of their residents.
Education
Limited access to quality education and low literacy rates are significant factors contributing to the identification of the poorest US state. Education plays a crucial role in economic development and social mobility, and its absence or inadequacy can perpetuate poverty.
States with high poverty rates often face challenges in providing equitable access to quality education. Underfunded schools, lack of resources, and shortage of qualified teachers can hinder students' ability to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary for success in higher education and the job market.
Moreover, low literacy rates can limit individuals' opportunities for personal growth and economic advancement. Illiteracy affects employability, earning potential, and overall well-being. It can also contribute to health disparities, as individuals with low literacy may struggle to understand health information and access healthcare services.
Addressing educational inequalities is essential for breaking the cycle of poverty. Investing in early childhood education, providing access to affordable and quality K-12 education, and supporting adult literacy programs are crucial steps towards improving educational outcomes and reducing poverty rates.
Healthcare
The absence of affordable healthcare and limited access to medical facilities are significant factors contributing to the identification of the poorest US state. Healthcare is a fundamental human right and plays a crucial role in the overall well-being of individuals and communities.
In states with high poverty rates, residents often face barriers in accessing quality and affordable healthcare services. Lack of health insurance, high medical costs, and shortage of healthcare providers can lead to delayed or neglected medical care, resulting in poor health outcomes and perpetuating poverty.
Limited access to medical facilities, particularly in rural areas, can further exacerbate healthcare disparities. Individuals may have to travel long distances or go without necessary medical care due to the absence of nearby hospitals or clinics. This lack of access can lead to delayed diagnoses, untreated chronic conditions, and increased mortality rates.
The connection between "Healthcare: Lack of affordable healthcare and limited access to medical facilities" and "what is the poorest US state" is evident in the vicious cycle it creates. Poverty can limit access to healthcare, which in turn can lead to poor health outcomes and further economic hardship. Addressing healthcare inequalities is therefore essential for breaking this cycle and improving the overall well-being of residents in the poorest US states.
Employment
High unemployment rates and low job availability are significant factors contributing to the identification of the poorest US state as they create a cycle of economic hardship and limited opportunities.
- Job scarcity
In states with high poverty rates, job opportunities may be scarce due to lack of economic development, business closures, or industry decline. This scarcity limits employment options for residents, leading to high unemployment rates.
- Low-paying jobs
Even when jobs are available, they may often be low-paying, providing insufficient income to cover basic necessities. This can lead to working poverty, where individuals are employed but still live below the poverty line.
- Lack of job skills
Poverty can perpetuate itself through lack of education and job skills. Individuals living in poverty may have limited access to quality education and training, hindering their ability to qualify for higher-paying jobs.
- Discrimination
Discrimination in the labor market can also contribute to high unemployment rates and low job availability for certain population groups, exacerbating poverty levels.
The connection between "Employment: High unemployment rates and low job availability" and "what is the poorest US state" is evident in the economic stagnation and limited opportunities it creates. This lack of employment and decent work can trap individuals and communities in a cycle of poverty, making it difficult to break free from economic hardship.
Housing
Inadequate housing conditions and lack of affordable housing are significant factors contributing to the identification of the poorest US state, as they create a cycle of poverty and limited opportunities.
In states with high poverty rates, residents often face challenges in securing safe and affordable housing. Substandard housing conditions, overcrowding, and lack of access to basic amenities can have detrimental effects on health, well-being, and economic stability. Overcrowded and unsanitary living conditions can lead to health issues, such as respiratory problems and infectious diseases, further perpetuating poverty.
Moreover, the lack of affordable housing can strain household budgets, leaving less money for other essential needs such as food, healthcare, and education. Families may be forced to live in substandard housing or spend a disproportionate amount of their income on rent, making it difficult to save, invest in education, or improve their economic situation. This lack of affordable housing options can trap individuals and families in a cycle of poverty, limiting their ability to achieve economic mobility.
The connection between "Housing: Inadequate housing conditions and lack of affordable housing" and "what is the poorest US state" is evident in the economic and social challenges it creates. Addressing housing inequalities is therefore essential for breaking this cycle and improving the overall well-being of residents in the poorest US states.
Infrastructure
Inadequate infrastructure, encompassing transportation, water, and sanitation, is a significant factor in determining the poorest US state. The absence of reliable infrastructure creates a cycle of poverty, hindering economic growth and social development.
Poor transportation infrastructure limits access to jobs, education, and healthcare, particularly in rural areas. Without adequate roads, bridges, and public transportation, individuals may struggle to reach employment opportunities or essential services. This lack of mobility perpetuates poverty, as individuals are unable to fully participate in the economy and improve their livelihoods.
In addition, the absence of clean water and sanitation systems poses severe health risks and economic challenges. Contaminated water sources can lead to waterborne diseases, exacerbating health issues and straining healthcare systems. Inadequate sanitation facilities can result in poor hygiene practices, contributing to the spread of disease and creating an environment conducive to poverty.
The connection between "Infrastructure: Poor infrastructure, including transportation, water, and sanitation" and "what is the poorest us state" lies in the fundamental role infrastructure plays in economic and social development. Investing in infrastructure can break the cycle of poverty by creating jobs, improving access to essential services, and fostering a healthier and more productive population.
Food security
In the context of identifying the poorest US state, food security plays a crucial role. Limited access to nutritious food and high rates of food insecurity are significant contributing factors that perpetuate poverty and hinder economic development.
- Economic disparities
Poverty is closely linked to food insecurity. Individuals and families living in poverty may have limited financial resources to purchase nutritious food, leading to reliance on low-cost, unhealthy options. This can result in poor nutrition and health problems, further exacerbating poverty.
- Lack of access to healthy food sources
In impoverished areas, access to supermarkets, farmers' markets, and other sources of fresh produce may be limited. This lack of access can make it difficult for residents to obtain nutrient-rich foods, leading to a reliance on processed and fast foods that are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and added sugars.
- Limited nutrition education
Individuals living in poverty may have limited access to nutrition education and resources. This can result in a lack of knowledge about healthy eating practices and the importance of a balanced diet, leading to poor food choices.
- Food insecurity and health disparities
Food insecurity is closely linked to health disparities. Individuals and families who are food insecure may experience higher rates of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. This can further strain healthcare systems and perpetuate poverty.
Addressing food insecurity in the poorest US states requires a multifaceted approach involving economic assistance, nutrition education programs, and investments in local food systems. By improving access to nutritious food and promoting healthy eating habits, we can break the cycle of poverty and improve the overall well-being of communities.
Safety
The prevalence of high crime rates and the absence of adequate public safety measures are significant factors contributing to the identification of the poorest US state. The connection between these factors and poverty is multifaceted and deeply rooted in the fabric of impoverished communities.
- Increased vulnerability and fear
High crime rates create an environment of fear and insecurity, making residents less likely to engage in activities that could improve their economic well-being, such as starting a business or seeking employment. The constant threat of crime can also lead to psychological trauma and diminished quality of life.
- Deterioration of local businesses and investments
Businesses are less likely to invest in areas with high crime rates, as the risk of property damage, theft, and employee safety concerns can outweigh potential profits. This lack of investment can further limit job opportunities and economic growth in impoverished communities.
- Strain on public resources
High crime rates can strain public resources, as law enforcement agencies struggle to maintain order and respond to emergencies. This can lead to reduced funding for other essential services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, further exacerbating poverty.
- Erosion of community trust
The lack of public safety and high crime rates can erode trust between community members and law enforcement. This can make it difficult to address crime effectively and create a sense of hopelessness and disengagement, perpetuating poverty.
Addressing the connection between "Safety: High crime rates and lack of public safety" and "what is the poorest US state" requires a comprehensive approach that includes community policing, crime prevention programs, and investments in education, employment, and social services. By creating safer neighborhoods and empowering residents, we can break the cycle of poverty and build stronger, more prosperous communities.
Economic opportunity
The connection between "Economic opportunity: Low levels of business investment and limited job growth" and "what is the poorest us state" lies in the fundamental role economic opportunity plays in addressing poverty and fostering economic well-being.
- Lack of investment and job creation
In the poorest US states, there is often a lack of investment in businesses and job creation. This can be due to various factors, such as a lack of attractive business incentives, poor infrastructure, or a shortage of skilled workers. The absence of investment and job opportunities perpetuates poverty, as individuals and families have limited options for economic advancement.
- Brain drain and population loss
When economic opportunities are scarce, talented individuals and families may migrate to other states or regions with better job prospects. This brain drain and population loss can further exacerbate poverty, as communities lose their most productive members and the tax base needed to fund essential services.
- Limited access to capital and resources
In impoverished communities, small businesses and entrepreneurs may face limited access to capital and resources, making it difficult to start or expand their businesses. This lack of access to financing and support hinders job creation and economic growth, perpetuating poverty.
- Skills gap and workforce development
The poorest US states often face a skills gap, where the available workforce lacks the skills and training necessary for high-paying jobs. This mismatch between skills and job requirements can lead to limited job opportunities and persistent poverty.
Addressing the connection between "Economic opportunity: Low levels of business investment and limited job growth" and "what is the poorest US state" requires a comprehensive strategy that includes investing in infrastructure, education, and workforce development. By creating a more favorable environment for business investment and job creation, we can break the cycle of poverty and build stronger, more prosperous communities.
FAQs
Poverty is a complex issue influenced by various socio-economic factors. Here are some commonly asked questions and answers regarding the poorest US state:
Question 1: What are the key indicators used to determine the poorest US state?
Key indicators include poverty rate, income levels, unemployment rate, access to healthcare and education, housing affordability, and crime rate. These factors collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of the economic well-being of a state's population.
Question 2: Which state consistently ranks as the poorest in the US?
Mississippi consistently ranks as the poorest state in the US based on multiple socio-economic indicators. It faces challenges such as persistent poverty, low per capita income, and limited economic opportunities.
Question 3: What are the root causes of poverty in the poorest US states?
Root causes include lack of job opportunities, low educational attainment, inadequate healthcare access, and limited affordable housing. These factors are interconnected and contribute to the cycle of poverty.
Question 4: How does poverty impact the residents of the poorest US states?
Poverty can lead to food insecurity, poor health outcomes, limited access to education and job opportunities, and increased crime rates. It can have long-lasting effects on individuals, families, and communities.
Question 5: What are some policy solutions to address poverty in the poorest US states?
Policy solutions include investing in education and job training, increasing access to affordable healthcare and housing, and promoting economic development. Addressing poverty requires a comprehensive approach that tackles its root causes.
Question 6: What can individuals do to help address poverty in the poorest US states?
Individuals can support organizations working to alleviate poverty, volunteer their time to help those in need, and advocate for policies that promote economic and social justice.
Understanding the poorest US state is crucial for developing targeted interventions and fostering economic growth. By addressing the root causes of poverty, we can work towards creating a more just and equitable society.
Transition to the next article section: Exploring the Impact of Poverty on Health Outcomes
Tips to Understand "What is the Poorest US State"
Understanding the concept of the poorest US state requires a multifaceted approach. Here are several tips to enhance your knowledge and perspective:
Tip 1: Examine Socioeconomic Indicators
Analyze key socioeconomic indicators such as poverty rate, income levels, education attainment, and healthcare access. These factors provide a comprehensive overview of a state's economic well-being.
Tip 2: Consider Historical Context
Explore the historical context that has shaped poverty levels in different US states. Factors such as economic policies, industrialization, and social inequality can influence poverty rates.
Tip 3: Analyze Policy Impact
Examine the impact of government policies and programs on poverty reduction. Evaluate the effectiveness of initiatives aimed at improving education, healthcare, and job opportunities.
Tip 4: Understand Interconnections
Recognize the interconnectedness of factors that contribute to poverty. Lack of education, limited job opportunities, and inadequate healthcare can perpetuate a cycle of poverty.
Tip 5: Utilize Reputable Sources
Rely on credible sources of information, such as government data, academic research, and non-partisan organizations, to gather accurate and unbiased information about poverty.
Tip 6: Engage in Critical Thinking
Engage in critical thinking to analyze information and draw informed conclusions. Avoid relying solely on superficial observations or emotional appeals.
Tip 7: Seek Diverse Perspectives
Consider multiple perspectives on poverty to gain a comprehensive understanding. Listen to the voices of those experiencing poverty, as well as experts and policymakers.
Summary: By following these tips, you can enhance your understanding of the concept of the poorest US state, its contributing factors, and potential solutions. A well-rounded perspective is essential for informed discussions and effective policymaking.
Conclusion
Comprehending the concept of the poorest US state requires a nuanced examination of various socioeconomic factors. By analyzing indicators such as poverty rate, income levels, education attainment, and healthcare access, we gain insights into the economic well-being of different states. Furthermore, considering historical contexts, policy impacts, and the interconnectedness of contributing factors provides a comprehensive understanding of poverty.
Addressing poverty necessitates critical thinking, reliance on credible sources, and consideration of diverse perspectives. Only through a thorough exploration of "what is the poorest US state" can we effectively develop and implement strategies to alleviate poverty and promote economic justice. This understanding is crucial for policymakers, community leaders, and individuals alike, as it empowers us to make informed decisions and work towards a more equitable society.
Unveiling The Truth: Natalie Reynolds Leaked - Discoveries And Insights
Unveil The Rich Tapestry Of Rubi Rose's Multiracial Heritage
Love Reconciled: Jeff Lewis And Stu Vorster's Navigating Relationship
ncG1vNJzZmirlZeyra3Ha2WapaNoe6W1xqKrmqSfmLKiutKpmJydo2OwsLmOsJ%2BarF2ewG7Ax55kqaefp7K0wIyuqmarpJbBpnrHraSl